Choline is one of the indispensable basic components in living organisms. It is generally considered as a kind of B vitamins (also known as vitamin B4). It has irreplaceable basic functions in the body, mainly in three aspects. : It is one of the components of the cell membrane; promotes the breakdown of fat (avoids fatty liver); transmits nerve signals. When the animal lacks choline, it will show choline deficiency: Poultry shows impaired growth; fatty infiltration of the liver and kidneys; short cheekbones, slippery sensation; increased mortality; reduced egg production rate; reduced egg size . Pigs showed slow growth; disordered behavior, neurological disorders; malnutrition, poor reproductive performance; fatty liver and so on. Therefore, satisfying the choline requirement in animals has important significance for maintaining the healthy growth and normal productivity of animals. Although choline is present in natural feed ingredients, its amount is insufficient to meet the daily growth needs of animals and must be added to the feed. In the feed industry, choline is usually added in the form of choline chloride. At present, the choline chloride additive in China is mainly 50% powder, and there are 60% powder and 70% water, but the most commonly used is 50% of the powder. The product is implemented in GB10818-89, and the content is determined as perchloric acid titration method. The principle of the assay is to first extract the choline chloride with methanol, evaporate the solvent, and then convert the choline chloride to acetate with mercury acetate. Hardly ionized mercury chloride is titrated with perchloric acid in an acetic acid medium to produce acetate. For true choline chloride, the choline chloride content measured by this method is accurate and reliable. However, in recent years, with the oversupply of the market, some unscrupulous manufacturers have incorporated other low-cost substances such as chlorides, ammonium salts or trimethylamine raw materials into choline chloride while depressing prices. The use of choline chloride in the detection of national standards can not find problems. If used in feed, it will have a great negative impact on the trust of feed manufacturers' feed quality and cause farmers to suffer economic losses. Therefore, how to effectively identify the adulteration of choline chloride, the real content of choline chloride has an important practical significance for feed mills. The author has accumulated some experience in this regard based on his work practices and reference to relevant information. The following summary will be made. At present, there are usually four kinds of methods for determining the choline chloride content in choline chloride powder at 50% in China: (1) Non-aqueous titration; (2) Ag method; (3) Nitrogen determination; (4) Tetraphenylboron Sodium gravimetric method. I. Method Introduction 1. Non-aqueous titration method (GB10818-89) Weigh 0.7g of sample dried at 80°C for 3h (weighed to 0.0002g), placed in a 250 ml conical flask, add 40 ml of methanol, shake well for 30 min. After filtration, the precipitate was washed three times with 20 ml, 15 ml, and 15 ml of methanol, and the filtrate and the washings were combined and evaporated to dryness on a water bath. 20ml of glacial acetic acid was added to the above flask to dissolve, 2ml of acetic anhydride was added, 10ml of mercury acetate test solution and two drops of crystal violet indicator solution were shaken and titrated with a perchloric acid standard solution until the solution was pure blue. At the same time do a blank test. 2, the amount of silver method (Mohr method) Weigh the sample 1.4g (called to 0.0002g), placed in a 100ml volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with water, shake, place 20min, filter, discard the initial filtrate, the exact amount Take 50ml of the filtrate in a 250ml flask, add 0.5ml of potassium chromate indicator solution, and titrate with 0.1ml silver nitrate standard solution until it is red. At the same time blank test. 3, the nitrogen method (1) Weigh the sample 3g (pronounced to 0.0002g), placed in 250ml dry flask, add water 100ml, fully shake 15min, filter, absorb the filtrate 10ml, according to Kjeldahl method first digestion Re-distillation measured total nitrogen N total. (2) Another filtrate 10ml in the digestive tube, add water 20ml, add 400g/L NaOH solution 20ml, directly in the nitrogen determination instrument distillation, determine the nitrogen content of N0. (3) Take 10ml of the filtrate in the digestive canal, add 400g/L NaOH solution (5ml), distill it on the electric furnace until it is free of alkaline gas (the pH test paper is neutral), digest it first by Kjeldahl method and then measure by distillation. Its nitrogen content is N1. 4. Accurately weigh 1 g sample of tetraphenylborate sodium gravimetric method (to be quasi-0.0002g), place it in a 100ml volumetric flask, add 80ml of water and fully shake it for 20min, dilute to volume with water, filter, discard the initial filtrate, and accurately take the filtrate 10ml in a 100ml beaker, add water 20ml, 1 drop of 10% AlCl3 solution, 20ml of 2% sodium tetraphenylborate solution, shake for 30min, filter on pre-weighed G4 core funnel, set in a constant temperature drying oven at 105°C Constant weight. Calculation: Choline chloride weight W1 = residue weight (g) 0.3298100/10. Choline chloride content = W1100/sample weight. 2. How to use the detection methods for adulteration identification in the laboratory to determine the true content of choline chloride. The first three of the above four methods are not directed to choline chloride. The specific structure or specific physical and chemical properties of the established, sodium tetraphenylboron method will be K +, NH4 + interference, for different adulterants, one of the methods used to detect may not be able to identify, so the specific test should be specific samples treat. The following summarizes how to use the detection methods for the identification of adulterates of choline chloride powders. 1, although the perchloric acid titration method is not a specific reaction of choline chloride, but in the test with this method, for the real raw material of choline chloride powder, after the solvent evaporates, the wall of the bottle of the triangle is translucent The crystallized product was clear after glacial acetic acid was dissolved, and the titration end point was obvious. If the bottle wall attachment is a thick layer of opaque material, the solution is turbid after the glacial acetic acid dissolves, and the titration end point is not obvious, although it can eventually become the color of the end point, but not a sudden leap between a drop of the sample. Innocentness is doubtful. 2, for the above method to detect suspicious samples, using the method of nitrogen determination. According to the formula C5H14NClO of choline chloride (its molecular weight is 139.63), theoretically 50% of the powder raw material has nitrogen content of 5%, so if the nitrogen content N is always low, it can be concluded as an adulterated sample. Under normal circumstances, N0 is very low, generally not more than 0.1%, equivalent to the blank value of the general test, N1≈N total. If not, it is an adulterated sample. The following are some of the sample nitrogen determination methods encountered by the author in his daily work. See the table below: Nitrogen determination test results Sample No. N Total 5.86% 5.02% 4.85% N0 5.06% 0.91% 0.08% N1 0.78% 4.10 % 4.80% In sample 1, N0≈N total, indicating that the sample is almost entirely trimethylamine, ammonium salts or other nitrogenous substances that can react with sodium hydroxide, and is false choline chloride. In sample 2, N0 is higher, indicating that the residue of trimethylamine in this sample is high, which is unqualified choline chloride. In sample 3, N1≈N total, it can be concluded that no ammonium salt, trimethylamine, or other nitrogenous substances that can react with sodium hydroxide are incorporated in the sample. For this sample, it needs to be further measured by the gravimetric method. We have encountered a sample with normal content determined by the nitrogen determination method and the silver determination method. When the titration is performed with the perchloric acid method, the titration end point is not so obvious. The results of these three methods are all about 55%, but they are measured by the gravimetric method. When the choline chloride content was only 27.1%, adulterated samples. 3. In the test, we also found that it was qualified by the gravimetric method, the perchloric acid method, and the silver method, but it was found to be an adulterated sample by the nitrogen determination method. N0 is high, N0≈N total. Third, the conclusion of the current market on the use of national standards for the detection of choline chloride content limitations, adulteration phenomenon. For different adulteration situations, it is not always possible to identify them using one of the above methods, and it is usually eliminated step by step in different ways. Therefore, for a choline chloride powder raw material, can not be tested according to the national standard even if it is completed, but also need to use different methods to further verify. Especially when the end point of a sample titrated with perchloric acid is not obvious, it must be taken seriously and further verified by several other methods. Only four kinds of methods have the same test results, can only pass the qualified conclusions and ensure the accuracy of the test results.
1.Good safety of gelatin-free.The first lyophilized Varicella Vaccine, containing no gelatin from animals, invented and produced in China. Getting rid of gelatin from varicella vaccine can significantly decrease the ratio of anaphylaxis incidence .
2.Long validity period by good stability. The first approved varicella vaccine with 36 months of validity period in the world. Adopting BH-2 stabilizer with own IP rights (Chinese patent granted No.: ZL200910138411.6, International patent application No.: PCT/CN2009/001405) greatly enhances the stability of the product and ensures the validity period for 36 months under the storage condition.
3.Better protection with high titer and immune eff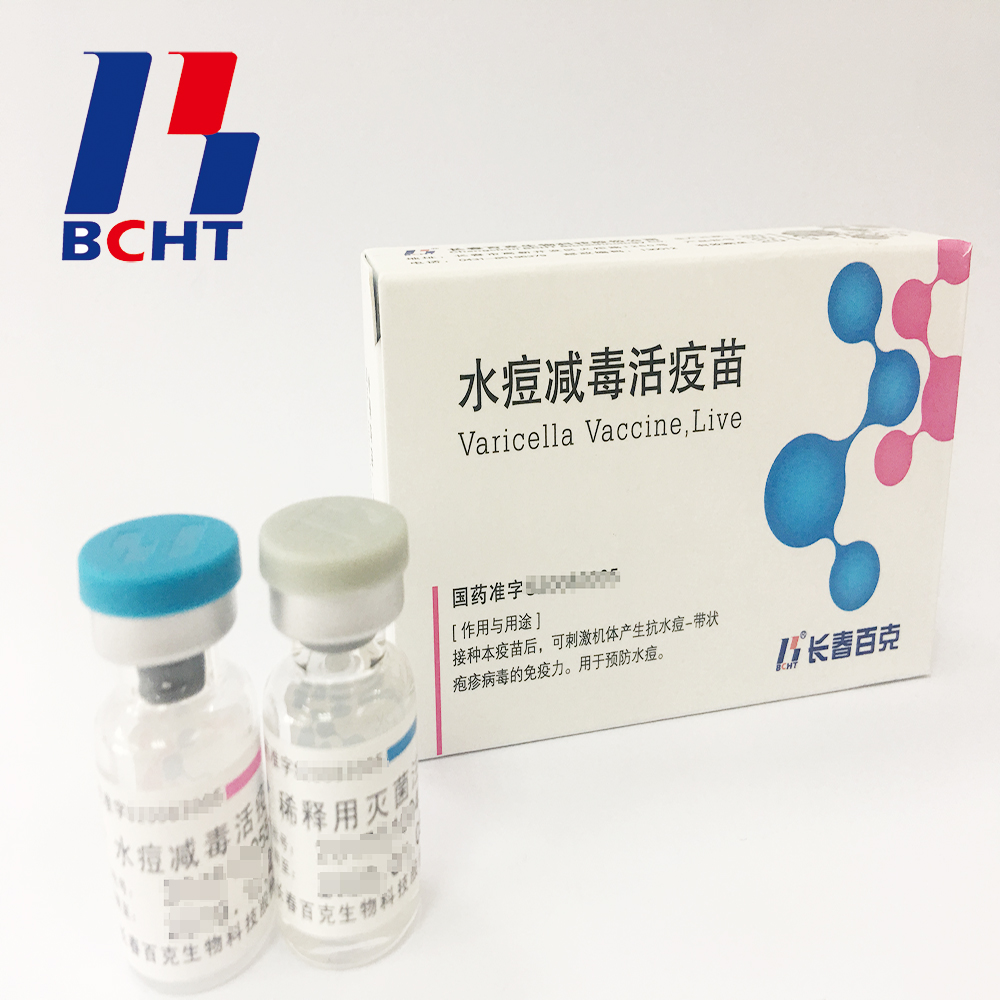 icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
Varicella Vaccine(Live)
Live Bioproducts Pharmaceutical,Live High Potency Medicine,Live Preventive Pharmaceutical,Varicella Biopharmaceutical Live
Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.ccbcht.net
 icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
