In recent years, the market price of small crabs has been falling all the way, big crabs have gone all the way, and supply is in short supply. If you want to raise a big crab, you must have a pollution-free crab as a guarantee. The demand for pollution-free crab species has increased throughout the country. Since 2000, we have used paddy fields to cultivate pollution-free crab species and achieved good results year after year. The average price of crab species was 1.25 yuan/ton, early-maturing crabs were 20 yuan/kg, rice was 1.4 yuan/kg, and the net income per 667 square meters of crabs and rice was as high as 15,000 yuan and the economic benefits were extremely significant. The cultivation techniques of pollution-free crabs in rice fields are summarized as follows:
I. Requirements and construction of rice fields Paddy fields require a quiet environment, convenient transportation, irrigation and drainage, water conservation and fertility, soil quality of loam, and water sources free from industrial wastewater, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides. The field project consists of Weigou, Tiangou, and crab seedling holding pools, accounting for more than 25% of the total rice field area. According to the needs of rice and crab symbiosis, a width of 3 meters wide and a width of 1 meter and a depth of 0.8 meters will be excavated at 1.5 to 2 meters away from the field. In the field, a crab ditch is excavated every 4 meters, so that the paddy field is in the shape of a “field†shaped piece. The ditch is 1 meter wide and 0.6 meters deep, and communicates with the ditch. On the south side of the field, a 20-meter square crab holding pool with a depth of 80 cm is built for every 667 m2 of paddy field, and it is used as a holding pond for intensive cultivation of large-eyed larvae or harvested crabs. The excavated earthwork was used to reinforce the field ridges, and plastic fences, No. 5 iron wires and stakes were used to build the fences and escape protection facilities on the fields. Paddy field water inlets and outlets also use mesh to prevent escape. After finishing the plots, 7.5 to 10 kilograms of quicklime per 667 square meters was used to kill the disease. At the same time, 0.5 kg of tea pods were soaked in warm water for a day and night to splash rice in order to kill wild fish. After the toxicity disappears, plants such as black algae and water peanuts are transplanted in ponds and trenches, covering 50% to 60% of the total area.
Second, the cultivation and management of rice selection of strong fertility, straw hard, not easy lodging, disease resistance and high yield of rice varieties. 15 days before transplanting, paddy fields were planted, 500 to 750 kg of fertilized farmyard fertilizer per 667 square meters, 20 to 25 kg of long-acting urea, and 35 to 40 kg of superphosphate were used as base fertilizers. 2 to 3 days before transplanting, the seedlings were given a high-efficiency pesticide to prevent the spread and spread of rice diseases and insect pests; transplanted seedlings were required to be robust and disease-free. Usually transplanted in shallow water, wide and dense plants, row spacing 30 to 35 cm, plant spacing 12 to 13 cm planted. Appropriately increase the planting density in the inside of the larvae and near the crab ditch, and exert the marginal advantage to increase rice yield.
Third, the cultivation and management of crab species In order to obtain a good harvest, the quality of crab seedlings is the key to the cultivation of pollution-free crab species. The production practice has proved that it is best to choose a pure Chinese mitten crab crab seedling that is robust, crawling, and tidy, with a specification of 150,000/kg. The crab raising pond was sterilized with 5kg of lime every 20 square meters in mid-April, and 12.5kg of cooked cow dung was used in late April. Paced bait was bred and water was injected immediately for 30cm. In early May, 0.5kg of crab seedling was released. After the crabs are in the pond, they are supplemented with eggs and roach at a ratio of 1:3 to 5 depending on the amount of natural food. They are fed 5 to 8 times a day and the rate of bait is 200%. When the crab grows to stage II, it uses minced fish, bean cake paste and bran, and is fed at a ratio of 2:1. It is fed 3 to 5 times a day, and the bait rate is 100%, with the growth of crab seedlings. Gradually increase the amount of feeding. After 15 days, artificial feed can be fed, formula: fish meal 25%, bean cake powder 25%, vegetable cake powder 23%, wheat flour 20%, bone meal 3%, yeast powder 2%, mineral additives 2%, another 0.1% added Chitin and 0.1% of complex vitamins are rolled into pelleted feeds containing 40% crude protein. Every day, 20 to 3 kilograms of feeding tanks are fed into the holding tanks, which are fed in the morning and evening. Crabs were cultivated until early June, and the earthworms in the holding ponds and rice fields were dug out. Water was poured from the inlets and the crabs followed the water flow into the rice fields. One month after the seedlings were thrown into the field, the feed was fed on the basis of 20% to 25% of the crab's body weight, and it was voted 1/3 at 8 o'clock in the morning and 2B at 6 o'clock in the evening. From the beginning of August to the middle of September, it is the growth control stage of crab species. Normally, it is fed once every night at 6 o'clock in the evening. In the first 20 days, the daily input of the batch material accounts for about 7% of the body weight, and the green grass accounts for 50% of the body weight. At 3% of body weight, grass accounts for 30% of body weight. After mid-September, it was the growth and maintenance phase of crab species, all of which were converted into plant feeds, such as raw pumpkin and cooked hawthorn, which accounted for 10% of the body weight. Every time before the arrival of the oyster shell, increase the amount of animal feed (more than 50%), found that the crab began to shell, can be poured 3 to 5 kg of lime, while the amount of water into the peanut, in order to increase the attachment of crab shell During the oyster shell will not change the water. Increase the number of food tables and feed them in small quantities.
In terms of water quality management, the holding pool shall be filled with water every 4 to 5 days. Each injection of water shall be 10 to 20 cm until the water depth is 60 to 80 cm. Change the water by 1/3 a day in hot weather. During the incubation period, the crabs insisted on starting daily oxygenation. After entering the field, the young crabs of Stage III and Stage V should try to raise the water level of the paddy field, change the water every 3 to 5 days, and change the water once a day at 10:00 in the summer and change the water volume to 1/3 to 1/2 of the field water body. The water level is raised to about 50 cm, and the water level or dehydration and baking fields are not arbitrarily changed so as to facilitate the growth of normal molting. In addition, the water temperature difference can not be greater than 3 °C. Every 15 to 20 days in the paddy field, 5 to 7.5 kilograms of quicklime is poured on every 667 square meters to kill the disease and supplement the calcium that the crab needs.
Adhere to the inspection of the field 1 to 2 times a day to check whether there is leftover bait, water quality changes, and anti-escape facilities and whether there is predilection, etc., to determine the amount of feed, change the amount of water and take appropriate measures to prevent disease. Crab disease is mainly prevention. From July to October, net 500 grams of fibrin insects are sprayed once a day to prevent ciliate disease and black shank disease; adhere to oxytetracycline and bait to prevent bacterial diseases, and the dosage is 50 kg. 100 grams of bait were fed and fed for 3 days per month; plants were washed before entering the field and disinfected with 25 g/m3 of strong chlorine spray to eradicate predators.
4. The catch of crab species and the habit of overwintering crab species can be caught by the running water method. In other words, when the paddy fields are released, the sleeve nets are trapped at the outlet. Or catch along the edge manually, and the remaining amount is captured after the field water is dried. The average catch rate can reach 95% or more. After the crabs are caught, they will be separated according to the size and size, and will be managed through winter. The method is to select the river or pond with better conditions, put the young crabs into crab cages or cages, submerge into the water, feed them regularly, and strengthen feeding and management. Strictly water-proof surface, and then enter into paddy fields, ponds or large water surface for crab breeding from March to April of the following year. You can also choose a crab pool with good conditions, direct wintering of crab species, strengthen winter management, make it safe for winter, and strive to eat and grow earlier in the following year. If crab species need to be sold, they are usually raised in cages or crab cages. Get up and go for the price.
I. Requirements and construction of rice fields Paddy fields require a quiet environment, convenient transportation, irrigation and drainage, water conservation and fertility, soil quality of loam, and water sources free from industrial wastewater, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides. The field project consists of Weigou, Tiangou, and crab seedling holding pools, accounting for more than 25% of the total rice field area. According to the needs of rice and crab symbiosis, a width of 3 meters wide and a width of 1 meter and a depth of 0.8 meters will be excavated at 1.5 to 2 meters away from the field. In the field, a crab ditch is excavated every 4 meters, so that the paddy field is in the shape of a “field†shaped piece. The ditch is 1 meter wide and 0.6 meters deep, and communicates with the ditch. On the south side of the field, a 20-meter square crab holding pool with a depth of 80 cm is built for every 667 m2 of paddy field, and it is used as a holding pond for intensive cultivation of large-eyed larvae or harvested crabs. The excavated earthwork was used to reinforce the field ridges, and plastic fences, No. 5 iron wires and stakes were used to build the fences and escape protection facilities on the fields. Paddy field water inlets and outlets also use mesh to prevent escape. After finishing the plots, 7.5 to 10 kilograms of quicklime per 667 square meters was used to kill the disease. At the same time, 0.5 kg of tea pods were soaked in warm water for a day and night to splash rice in order to kill wild fish. After the toxicity disappears, plants such as black algae and water peanuts are transplanted in ponds and trenches, covering 50% to 60% of the total area.
Second, the cultivation and management of rice selection of strong fertility, straw hard, not easy lodging, disease resistance and high yield of rice varieties. 15 days before transplanting, paddy fields were planted, 500 to 750 kg of fertilized farmyard fertilizer per 667 square meters, 20 to 25 kg of long-acting urea, and 35 to 40 kg of superphosphate were used as base fertilizers. 2 to 3 days before transplanting, the seedlings were given a high-efficiency pesticide to prevent the spread and spread of rice diseases and insect pests; transplanted seedlings were required to be robust and disease-free. Usually transplanted in shallow water, wide and dense plants, row spacing 30 to 35 cm, plant spacing 12 to 13 cm planted. Appropriately increase the planting density in the inside of the larvae and near the crab ditch, and exert the marginal advantage to increase rice yield.
Third, the cultivation and management of crab species In order to obtain a good harvest, the quality of crab seedlings is the key to the cultivation of pollution-free crab species. The production practice has proved that it is best to choose a pure Chinese mitten crab crab seedling that is robust, crawling, and tidy, with a specification of 150,000/kg. The crab raising pond was sterilized with 5kg of lime every 20 square meters in mid-April, and 12.5kg of cooked cow dung was used in late April. Paced bait was bred and water was injected immediately for 30cm. In early May, 0.5kg of crab seedling was released. After the crabs are in the pond, they are supplemented with eggs and roach at a ratio of 1:3 to 5 depending on the amount of natural food. They are fed 5 to 8 times a day and the rate of bait is 200%. When the crab grows to stage II, it uses minced fish, bean cake paste and bran, and is fed at a ratio of 2:1. It is fed 3 to 5 times a day, and the bait rate is 100%, with the growth of crab seedlings. Gradually increase the amount of feeding. After 15 days, artificial feed can be fed, formula: fish meal 25%, bean cake powder 25%, vegetable cake powder 23%, wheat flour 20%, bone meal 3%, yeast powder 2%, mineral additives 2%, another 0.1% added Chitin and 0.1% of complex vitamins are rolled into pelleted feeds containing 40% crude protein. Every day, 20 to 3 kilograms of feeding tanks are fed into the holding tanks, which are fed in the morning and evening. Crabs were cultivated until early June, and the earthworms in the holding ponds and rice fields were dug out. Water was poured from the inlets and the crabs followed the water flow into the rice fields. One month after the seedlings were thrown into the field, the feed was fed on the basis of 20% to 25% of the crab's body weight, and it was voted 1/3 at 8 o'clock in the morning and 2B at 6 o'clock in the evening. From the beginning of August to the middle of September, it is the growth control stage of crab species. Normally, it is fed once every night at 6 o'clock in the evening. In the first 20 days, the daily input of the batch material accounts for about 7% of the body weight, and the green grass accounts for 50% of the body weight. At 3% of body weight, grass accounts for 30% of body weight. After mid-September, it was the growth and maintenance phase of crab species, all of which were converted into plant feeds, such as raw pumpkin and cooked hawthorn, which accounted for 10% of the body weight. Every time before the arrival of the oyster shell, increase the amount of animal feed (more than 50%), found that the crab began to shell, can be poured 3 to 5 kg of lime, while the amount of water into the peanut, in order to increase the attachment of crab shell During the oyster shell will not change the water. Increase the number of food tables and feed them in small quantities.
In terms of water quality management, the holding pool shall be filled with water every 4 to 5 days. Each injection of water shall be 10 to 20 cm until the water depth is 60 to 80 cm. Change the water by 1/3 a day in hot weather. During the incubation period, the crabs insisted on starting daily oxygenation. After entering the field, the young crabs of Stage III and Stage V should try to raise the water level of the paddy field, change the water every 3 to 5 days, and change the water once a day at 10:00 in the summer and change the water volume to 1/3 to 1/2 of the field water body. The water level is raised to about 50 cm, and the water level or dehydration and baking fields are not arbitrarily changed so as to facilitate the growth of normal molting. In addition, the water temperature difference can not be greater than 3 °C. Every 15 to 20 days in the paddy field, 5 to 7.5 kilograms of quicklime is poured on every 667 square meters to kill the disease and supplement the calcium that the crab needs.
Adhere to the inspection of the field 1 to 2 times a day to check whether there is leftover bait, water quality changes, and anti-escape facilities and whether there is predilection, etc., to determine the amount of feed, change the amount of water and take appropriate measures to prevent disease. Crab disease is mainly prevention. From July to October, net 500 grams of fibrin insects are sprayed once a day to prevent ciliate disease and black shank disease; adhere to oxytetracycline and bait to prevent bacterial diseases, and the dosage is 50 kg. 100 grams of bait were fed and fed for 3 days per month; plants were washed before entering the field and disinfected with 25 g/m3 of strong chlorine spray to eradicate predators.
4. The catch of crab species and the habit of overwintering crab species can be caught by the running water method. In other words, when the paddy fields are released, the sleeve nets are trapped at the outlet. Or catch along the edge manually, and the remaining amount is captured after the field water is dried. The average catch rate can reach 95% or more. After the crabs are caught, they will be separated according to the size and size, and will be managed through winter. The method is to select the river or pond with better conditions, put the young crabs into crab cages or cages, submerge into the water, feed them regularly, and strengthen feeding and management. Strictly water-proof surface, and then enter into paddy fields, ponds or large water surface for crab breeding from March to April of the following year. You can also choose a crab pool with good conditions, direct wintering of crab species, strengthen winter management, make it safe for winter, and strive to eat and grow earlier in the following year. If crab species need to be sold, they are usually raised in cages or crab cages. Get up and go for the price.
Hangwei is a very professional manufacture of orthopedics implants.
We dedicate in the research an develop the most highely convinent and minimally invasive products.
At the same time,we would meet most of customer's need,produce instrument according to your demand.
LCP can be used for fixation and implantation of various orthopaedic or traumatic diseases,such as humerus,ulna,radius,femur,tibia,fibula,clavicle,calcaneal,scapula,pelvic.
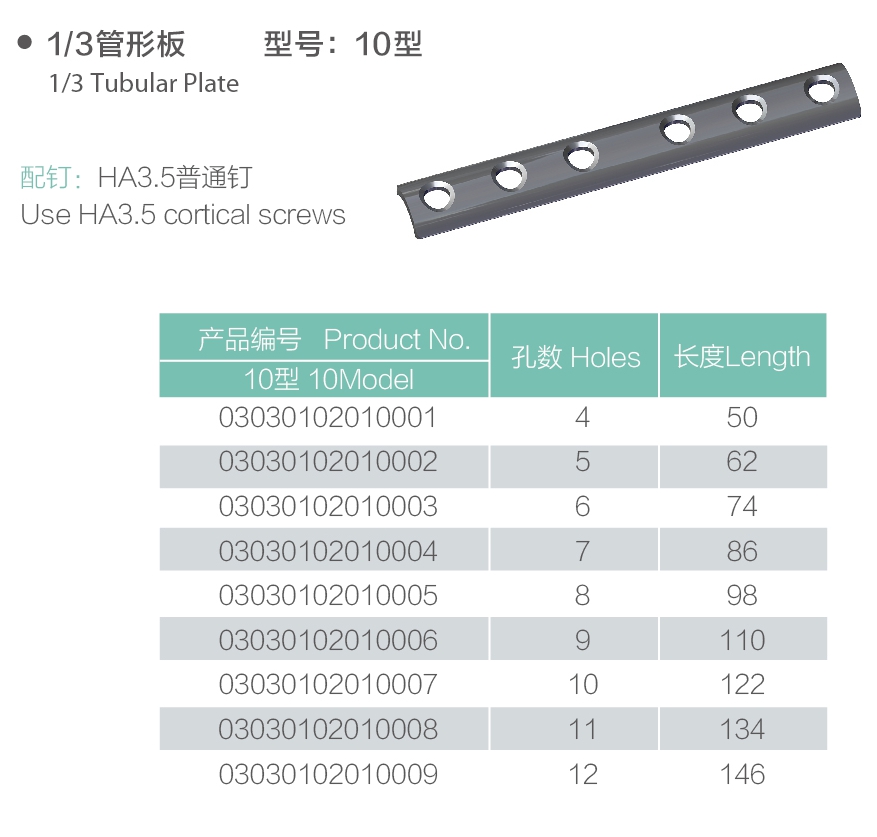
Locking Compression Plate,LCP Straight Titanium Locking Plate,1/3 Tubular Locking Plate Trauma,Quality Locking Compression Plate
Shandong Hangwei Orthopedics Medcial Instrument Co., Ltd. , http://www.hangweimedical.com
