Ginger is an indispensable vegetable in the table of the people of our country. Therefore, the area of ​​ginger planted in China is now expanding. Shandong Province is a province with a large area of ​​ginger planting in China, and the planting area accounts for about a quarter of the country's planted area. The various mineral elements required for the growth of ginger, in addition to absorbing the mineral elements present in the soil, also require the supply of fertilizer. Fertilization is one of the key factors for obtaining high yield of ginger. The following is a key technology for fertilization of pollution-free ginger.

1 Determine reasonable nutrient usage
The recommended nutrient dosage of ginger needs to consider soil, climate, topography and other factors. The amount of ginger used in this paper is recommended to be based on the soil nutrient system management concept.
Nutrient absorption = target yield × unit yield nutrient uptake (1)
Nutrient recommendation amount = nutrient absorption amount × correction factor (2)
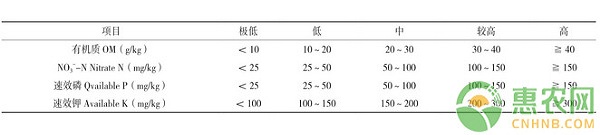
Three parameters are involved in equations (1) and (2), and the method for determining the target yield is usually 120% of the average yield of the proposed three-year plot (region). The results showed that the nutrient uptake of ginger was: nitrogen (N) 7.0 kg/t, phosphorus (P2O5) 2.0 kg/t, and potassium (K2O) 10.5 kg/t. As for the correction coefficient, under normal conditions, the correction coefficients of N, P2O5 and K2O are α=1.35, β=1, γ=1 respectively; under high fertility level, the correction coefficients of N, P2O5 and K2O are α= 1.05, β=0.8, γ=0.8; under low fertility level, the correction coefficients of N, P2O5 and K2O are α=1.55, β=1.2, γ=1.2; the evaluation criteria of soil level can refer to the evaluation of facility soil fertility determined by Huang Shaowen et al. Standard, see Table 1.
2 Choose the right fertilizer variety
Fertilizer varieties can be divided into organic fertilizers and inorganic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers can be divided into piled and cooked livestock and poultry manure, commercial organic fertilizers (including bio-organic fertilizers, etc.), and other organic fertilizers (including straw, grass ash, waste slag, oil). Slag, etc.; Fertilizer can be divided into traditional fertilizer (single fertilizer, compound fertilizer, medium and trace elements, etc.) and new chemical fertilizer (water soluble fertilizer, slow release fertilizer, amino acid fertilizer, humic acid fertilizer, etc.). Various fertilizers have their own advantages, and the correct choice of fertilizer helps to improve fertilizer utilization.
1 Select fertilizer varieties according to the law of nutrient demand. Ginger requires a large amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and other medium and trace elements such as calcium, magnesium, zinc and boron. All kinds of elements must be properly combined to obtain the desired benefits. After determining the recommended amount of fertilization for ginger, the nutrient absorption ratio of ginger can be used as the basis for selection of the variety. Studies have shown that ginger has a high absorption of nitrogen and potassium, a low absorption of phosphorus, and a ratio of absorption of NPK of 1:0.10 to 0.30:1.20 to 1.50. According to the nutrient demand and fertilizer nutrient content of each growth period, calculate the total amount of each fertilizer used, and record the amount of each fertilizer (including organic fertilizer, commercial organic fertilizer, etc.); The absorption ratio is not consistent, so the amount of fertilizer can be slightly adjusted each time; in view of the low phosphorus absorption ratio, the top dressing should use low-phosphorus compound fertilizer (flushing fertilizer) or even no phosphate fertilizer.
While determining the varieties of ginger NPK fertilizers, it is also necessary to appropriately select medium and trace element fertilizers such as silicon, magnesium, calcium and zinc according to the demand of ginger for medium and trace elements and the content of trace elements in soil.

2 Select the fertilizer variety according to the fertilization method. Different fertilizer varieties, the conversion after application into the soil and the effectiveness of the season are different, so it should be based on the nutrient release law of the fertilizer to study which fertilization method is applicable. For example, in the ginger seedling stage, it is in the small arch shed, and root growth is crucial. Therefore, high-phosphorus water-soluble fertilizer and water-soluble fertilizer containing functional active substances such as humic acid can be selected. For example, in the topdressing stage, the small arch shed has been removed, and the fertilization should be carried out in combination with the soil. At this time, compound fertilizer and compound fertilizer can be used. After the soil cultivation, according to the principle of labor saving, the topdressing method usually adopts the method of fertigation, such as flushing. , sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, etc., at this time usually apply different proportions of nitrogen and potassium water soluble fertilizer (pre-high nitrogen, late high potassium), medium amount of water soluble fertilizer, trace element water soluble fertilizer and functional fertilizer.
3 organic and inorganic application. Organic fertilizer has the characteristics of fertility, long-term fertilizer, low nutrient content, high nutrient content, fast release, and lack of stamina. When selecting fertilizers, it should be applied organically and inorganically.
Table 1 Ginseng soil nutrient content classification reference standard
3 correct fertilization method
Ginger fertilization methods include basic application, ditching and fertilization, fertigation and fertilization. The basic application is applied to the base fertilizer, and the latter three are suitable for top dressing.
3.1 Kisch
The base fertilizer is generally applied in combination with soil tillage or soil preparation before planting. The base fertilizer input is generally based on organic fertilizer, and the manure of composted livestock and poultry is 5-7 m3/667 m2, and the commercial organic fertilizer is 1~1.5t/667m2, supplemented by a small amount of chemical fertilizer. The organic fertilizer is preferably a mixture of livestock manure and straw, or high-carbon organic fertilizer; the nutrient input of fertilizer accounts for about 20% of the total input fertilizer; for degraded soil, the appropriate amount of soil conditioner can also be applied to It plays a role in changing soil and promoting root growth.
The application methods of ginger base fertilizer include application and application. Fertilizer application is done before trenching in the unfinished land. The fertilizer is spread to the surface. The fertilizer is mixed into the soil with tillage. This method is simple, labor-saving and uniform in fertilizer application. It is suitable for coarse application and low nutrient content. Organic fertilizer (soiled livestock and poultry manure, etc.). Chemical fertilizers, bio-organic fertilizers, etc. are suitable for ditch application, and are applied after the ditching of the ginger soil to the time of sowing. The advantage of the ditch application is that the root system can be stretched.
3.2 Ditching and fertilizing
Ginger usually needs to be soiled 2 to 3 times in the whole life. For example, in Qingzhou City, Shandong Province, the small arch shed is uncovered in the middle and late June, the first ditch is fertilized, and the other is in the middle and late July, and the compound fertilizer is usually used before the soil is cultivated. Spread the left and right sides of the ginger tree in the ditch (direction of the row), and then use a special earth-boring tool to cultivate the soil.
3.3 Fertigation
Irrigation and fertilization is usually divided into traditional irrigation-free fertilization (with water) and modern water-fertilizer integration technologies (such as micro-spraying and drip irrigation), which can be applied after ginger cultivation and before harvest. With water, it is usually applied to the beginning of the field irrigation to dissolve the fertilizer in water, and then evenly irrigated with water. Micro-spraying and drip irrigation are methods of applying fertilizer by using water and fertilizer integration technology. At present, production is still dominated by water, but the integrated technology of water and fertilizer is a new technology with broad prospects in the future production of ginger.
3.4 external fertilization
Ginger relies mainly on roots to absorb nutrients, but leaves can also absorb foreign substances, such as gases, nutrients, pesticides, etc. The leaves absorb nutrients and absorb nutrients into the ginger plants like roots. In addition to the nutrients that can be absorbed from the roots, the nutrient that can absorb nutrients through the leaves is called foliar nutrition. The measure of applying fertilizer on the surface of vegetative bodies other than ginger roots is called extra-root fertilization, which is commonly referred to as foliar fertilization. The advantages of foliar fertilization include: 1 fast nutrient absorption; 2 little dependence on soil conditions; 3 foliar spray can be combined with pesticides, plant growth regulators and other active substances.
When the ginger leaves are fertilized, the fertilizer concentration should not be too high or too low. Usually, the large amount of elements is 0.2% to 2%, and the trace elements are 0.01% to 0.2%. Generally, foliar spraying is carried out before 9:00 am or after 4:00 pm in a windless sunny day. At this time, the leaf surface temperature is low, the light is weak, the water evaporation is weak, and the leaves can maintain a long wet time, which is beneficial to Improve the effect of foliar application. When spraying, focus on the growing upper middle leaves, especially the back of the leaves. Because ginger has a long growth period, it can be sprayed 2 to 3 times in the middle and late stages of growth and development (September and October).
4 correct fertilization time
Fertilization time should be consistent with the critical period of ginger nutrient demand, in order to meet the growth requirements of ginger, improve the fertilizer and fertilizer utilization rate, and lay the foundation for high yield. Ginger in Shandong Province is generally sown in early April and harvested around mid-October. The whole growth process of ginger is basically a process of vegetative growth, so its growth has obvious stages, but the division is not strict. According to its growth characteristics and growing season, it is divided into germination stage, seedling stage, vigorous growth period and rhizome dormancy. The period is 4 periods.

4.1 germination period
From the beginning of the sprouting of the ginger seedlings, to the first piece of ginger leaves, including the whole process of germination and emergence, it takes 40 to 50 days. During the germination period of ginger, the nutrients stored in the ginger are mainly germinated and grow, the growth rate is slow, and the growth amount is also small, accounting for only 0.24% of the total growth in the whole period. The nutrient demand in this period is less, basically no fertilization is required, but The use of functional fertilizers such as amino acid fertilizers and humic acid fertilizers to promote root growth lays the foundation for the vigorous growth of later plants.
4.2 Seedling stage
From the beginning of the exhibition leaves, to the two large side branches, commonly known as the "three scorpion" period, the morphological sign of the end of the seedlings needs 65 to 75 days, such as the Qingzhou City of Shandong Province generally around June 20. During this period, it was transformed from a heterotrophic form that relied on maternal nutrition to an autotrophic form in which ginger seedlings were able to absorb nutrients and make nutrients and basically live independently. In this period, the main stem growth and hair roots are dominant, the growth rate is slow, and the growth is not large. The growth in this period accounts for about 1/10 of the total growth in the whole period, and the absorbed N, P2O5 and K2O accounts for the total absorption. About 14% of the amount. The N, P2O5, K2O and other nutrients required in this period are also mainly provided by the base fertilizer. Therefore, the application of the base fertilizer and fertilizer should be paid attention to, and the application amount accounts for about 20% of the total fertilizer application.
4.3 prosperous growth period
From the "three-pound period" (before and after the removal of the arch shed), the above-ground stems and shoots and the underground rhizomes enter the vigorous growth period until the harvest takes 70-75 days. During this period, the main growth rate is greatly accelerated. Branches, the number of leaves also increased accordingly. The number of leaves grown in this period is 6 to 7 times that of the seedling stage. As the number of leaves increases, the leaf area also increases dramatically. On the other hand, the underground rhizome also rapidly expands. In this period, the growth of the plant accounts for more than 90% of the total growth, which is the key growth period of fertilization. From the perspective of the growth center, this period is obviously divided into two stages: before the first ten days of September, it is still the growth of stems and leaves in the early stage of growth or the period of growth, and the fertilization is mainly based on nitrogen fertilizer. Fertilization; after the first ten days of September, the growth center has been transferred to the rhizome, and the nutrients produced by the leaves are mainly transported to the rhizome to accumulate to form a product. Therefore, the growth of the rhizome is dominant at this time, which is the late growth period or the rhizome expansion period. Potash is mainly used for fertilization, and the main fertilization methods are fertigation and fertilization.
4.4 rhizome dormancy
After the ginger is harvested, it is stored in the wolfberry and kept in a dormant state. At this stage, no fertilizer is used.
5 correct fertilization position
Ginger roots are the main organ for absorbing nutrients. Therefore, the application of fertilizer can neither be too far from the root nor too close to the root. When the fertilizer is applied to the ditch, it is generally spread at a distance of about 10 cm from the ginger plant, and the fertilizer is applied to the soil, and then the soil is sealed and ridged. Although the production farmers are accustomed to traditional fertigation techniques, this method is not recommended. If fertigation is used, it is recommended to use water and fertilizer integration technologies such as sprinkler irrigation and drip irrigation. Root fertilization should be focused on the growing upper middle leaves, especially the back of the leaves.
Based on the principle of scientific fertilization, the above content systematically summarizes the scientific fertilization technology of pollution-free ginger from the perspective of the recommended amount of ginger fertilization, the choice of fertilizer variety, the correct fertilization method, the correct fertilization time and the correct fertilization position. In order to improve the level of scientific fertilization technology of farmers, and achieve the goal of fertilizer production, high yield, high efficiency, high quality and environmental protection.
Frozen Shelled shrimps,Frozen Bamboo shrimp,Frozen Red shrimp
Zhejiang ocean family co.,ltd , https://www.ocean-family.com
